Our Promise
Trustworthy Medical Care
Get your care delivered by a board-certified physician with an experience of over 24 years
Book Your Appointment
Whenever you need to, simply call us or book your appointment online
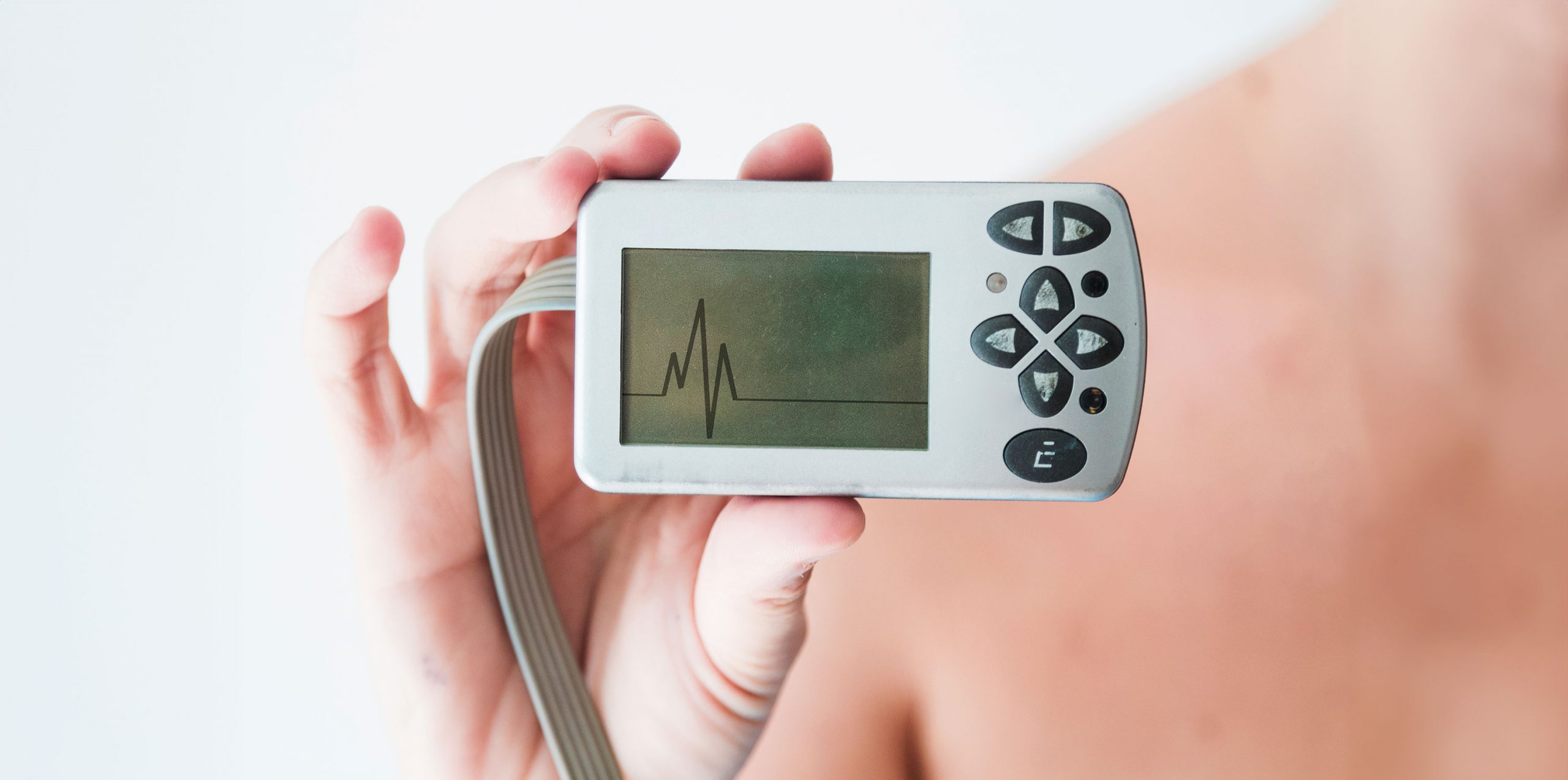
Enter the Holter monitor – a remarkable invention in the world of cardiac healthcare. Small in size but significant in impact, the Holter monitor serves as a vigilant guardian of heart health, offering insights that traditional methods might miss. It’s like having a miniature cardiac detective attached to you, meticulously recording every beat and rhythm of your heart. The data collected by this device is a treasure trove of information, providing a detailed picture of how your heart functions over an extended period, typically 24 to 48 hours.
• Name: Sarah Thompson
• Background: Sarah, a 42-year-old office manager with no significant cardiovascular history, began experiencing occasional palpitations. Concerned about her heart health, she sought medical advice.
Sarah’s palpitations posed a diagnostic challenge as they occurred sporadically, making it difficult to capture irregularities during traditional ECG tests. The fleeting nature of her symptoms demanded a more prolonged monitoring solution.
Recognizing the limitations of conventional testing, Sarah’s cardiologist recommended a 24-hour Holter monitor. This portable device offered continuous heart activity monitoring, capturing data throughout her daily activities and sleep, providing a comprehensive overview of her cardiac function.
Sarah underwent comprehensive education on Holter monitor usage. In addition to wearing the device, she maintained a diary, logging daily activities and symptoms. This dual approach aimed to correlate symptoms with recorded data, enhancing the diagnostic value of the monitoring process.
While the Holter monitor was non-invasive, Sarah faced initial discomfort wearing the device. Additionally, consistently logging activities posed a challenge. However, these challenges were minor compared to the potential insights the monitor could provide.
The 24-hour monitoring revealed episodes of arrhythmia during periods of increased stress at work. Detailed analysis by the healthcare team identified triggers for Sarah’s palpitations, leading to personalized treatment planning. Lifestyle modifications and stress management techniques were prescribed, resulting in a significant reduction in arrhythmia episodes during follow-up monitoring.
Before Holter monitoring, Sarah experienced palpitations 3-4 times a week, with high stress levels. After intervention, palpitations reduced to once a week, and her stress levels moderated, contributing to an improved overall quality of life.
Sarah reported feeling more in control of her health and appreciated the non-invasive nature of the monitoring. She expressed gratitude for the personalized strategies that significantly improved her symptoms.
This case highlights the instrumental role of Holter monitors in diagnosing and managing cardiac issues with sporadic symptoms. Continuous monitoring, coupled with personalized interventions, led to a tangible improvement in the patient’s quality of life, emphasizing the importance of tailored approaches in cardiac care.
A Holter monitor is a sophisticated yet user-friendly device in the realm of cardiac care. This device comprises small electrodes, resembling plastic patches, that adhere to specific points on your chest and abdomen. These electrodes are connected to the monitor via wires, facilitating the continuous recording of your heart’s electrical activity. This method is non-invasive and painless, as no electricity is sent into the body.
1. Symptoms Not Captured by Standard EKG: If a patient experiences symptoms like palpitations, chest pain, shortness of breath, skipped beats, or light-headedness, and these are not satisfactorily explained by a standard EKG, a Holter monitor may be recommended.
2. Unexplained Syncopal Episodes: Patients who have experienced unexplained fainting (syncope) or transient episodes of cerebral ischemia, which could potentially be related to cardiac rhythm disturbances, may benefit from Holter monitoring.
3. Cardiac or Conduction Disorders: Individuals diagnosed with significant cardiac or conduction disorders might require Holter monitoring as part of their evaluation and management. This continuous monitoring can provide detailed insights into the heart’s functioning over an extended period, helping in better diagnosis and treatment planning.
4. Heart Conditions with High Risk of Arrhythmias or Ischemia: For patients with heart conditions that are associated with a high incidence of serious cardiac arrhythmias or myocardial ischemia, a Holter monitor can be a crucial part of the evaluation. It helps in understanding the heart’s rhythm and its response to daily activities and stressors.
5. Evaluating the Effect of Cardiac Medications: If a patient is on cardiac medication that affects the electrical conduction system of the heart, Holter monitoring may be necessary to evaluate the effect of these medications on the patient’s cardiac rhythm and conduction system.
6. Pacemaker Functionality Checks: Patients with pacemakers who show clinical signs suggesting possible malfunction of the device may also be advised to undergo Holter monitoring. This is to ensure that the pacemaker is functioning correctly and managing the heart’s rhythm as intended.
A Holter monitor is a highly effective tool for diagnosing a variety of heart conditions, particularly those that may not be detected during a short-term ECG test. Here are some of the key conditions it helps identify:
1. Arrhythmias: Arrhythmias, or irregular heartbeats, are among the primary conditions detected by a Holter monitor. These include atrial fibrillation, bradycardia (slow heartbeat), tachycardia (fast heartbeat), and premature ventricular contractions (PVCs), which are extra, abnormal heartbeats originating in the ventricles.
2. Heart Palpitations and Unexplained Dizziness: Heart palpitations, often described as the heart racing or fluttering, and unexplained dizziness, are symptoms that can be linked to underlying heart rhythm issues. A Holter monitor helps in pinpointing these symptoms to specific heart rhythm abnormalities.
3. Evaluating Heart’s Oxygen Supply and Medication Effectiveness: The monitor also provides insights into how well the heart is getting oxygen and how effectively heart medications are working. This is crucial for patients with known heart conditions who are on medication.
4. Pacemaker Functionality: For patients with pacemakers, a Holter monitor can be used to assess how well the pacemaker is managing the heart’s rhythm.
5. Identifying Infrequent Arrhythmias: In cases where arrhythmias are infrequent, a standard ECG might not detect heart failure. A Holter Monitor Uses extend the monitoring period (24 to 72 hours or even longer), increasing the likelihood of capturing these sporadic events.
6. Further Diagnostic Steps: If a standard Holter monitor does not capture irregular heart rhythms, a healthcare provider might recommend an event recorder. This device, worn for a longer period (up to several weeks), allows patients to record their heart’s activity when they feel symptoms, providing further diagnostic information.
Function and Usage:
• Typically conducted in a doctor’s office, clinic, or hospital room, an EKG gives crucial information about the heart’s electrical activity. It shows if the electrical activity is normal, slow, fast, or irregular, and whether parts of the heart are enlarged or overworked.
• In contrast, a Holter monitor is a portable device used for continuous ECG monitoring over several days. It is particularly useful for detecting cardiac events such as atrial fibrillation and suspected stroke that may not be captured during the brief period of an EKG.
Recording Duration:
• The EKG provides a snapshot of the heart’s activity at a single point in time. It is extremely valuable for diagnosing arrhythmias but is limited to capturing heart activity only during the test. This poses a challenge for intermittent arrhythmias that may not occur during the EKG.
• The Holter monitor, however, records heart activity continuously, typically for 24 to 48 hours, and sometimes longer. This feature allows it to capture intermittent arrhythmias and correlate them with the patient’s symptoms. Even asymptomatic episodes are recorded, providing a comprehensive picture of heart activity.
Scope of Monitoring:
• The EKG is an essential, noninvasive diagnostic tool for many common heart problems in people of all ages. However, it may not always provide a comprehensive result, especially for conditions that manifest intermittently.
• The Holter monitor offers a more complete picture of heart activity, necessary for the diagnosis of certain cardiac conditions. Its continuous recording is more likely to detect irregularities that might be missed by an EKG.
• Apart from traditional EKGs and Holter monitors, there are newer technologies like smartwatches and insertable cardiac monitor uses. For instance, the Apple Watch can screen for asymptomatic events and record ECG rhythm strips on demand. However, they have limitations like false positive detections and require careful usage.
• Insertable cardiac monitors provide very long-term monitoring, up to three years or so. They can detect significant arrhythmias and save recordings automatically, but they require an invasive procedure for insertion and removal.
• A technician attaches the monitor and provides instructions. The setup involves attaching electrodes to the chest. These electrodes are small, round, sticky patches that record the heart’s electrical activity. In some cases, the technician may need to shave areas of the chest to ensure the electrodes attach firmly.
• The technician assists in putting on the monitor and connecting it to the electrodes. They provide guidance on how to care for the monitor. The monitor is typically carried in a pocket or bag, or worn on a strap like a purse or on the waist.
• Patients can engage in most of their usual activities while wearing the monitor. However, they should avoid bathing, showering, swimming, undergoing X-rays, and being near high-voltage areas or metal detectors to prevent damage to the device or interference with its functioning.
• The wearer is advised to keep a diary of activities and any symptoms experienced, such as shortness of breath, chest pain, or irregular heartbeats. This diary helps correlate any symptoms with changes in the heart’s electrical activity recorded by the Holter monitor.
• After wearing the monitor for the prescribed 24- or 48-hour period, it is returned to the technician. The technician then processes the records, including the EKG data and the patient’s notes, and prepares a report for the healthcare provider.
In conclusion, the Holter monitor is a pivotal tool in cardiac health, providing detailed and continuous analysis of heart rhythms over an extended period. Its ability to detect and characterize various arrhythmias, assess the effectiveness of medications, and identify potential cardiac conditions is invaluable. The correlation of arrhythmias with patient symptoms offers a deeper understanding of each individual’s cardiac health, enabling personalized medical interventions.
Based on the insights provided in this blog about the Holter monitor and its significance in cardiac health, Dr. Ellen Mellow, with her expertise in cardiology, can offer personalized care and detailed analysis of Holter monitor results. Her knowledge and experience in interpreting these results can be crucial in diagnosing and managing various heart conditions effectively, ensuring patients receive the most informed and tailored cardiac care possible.
Get your care delivered by a board-certified physician with an experience of over 24 years
Whenever you need to, simply call us or book your appointment online